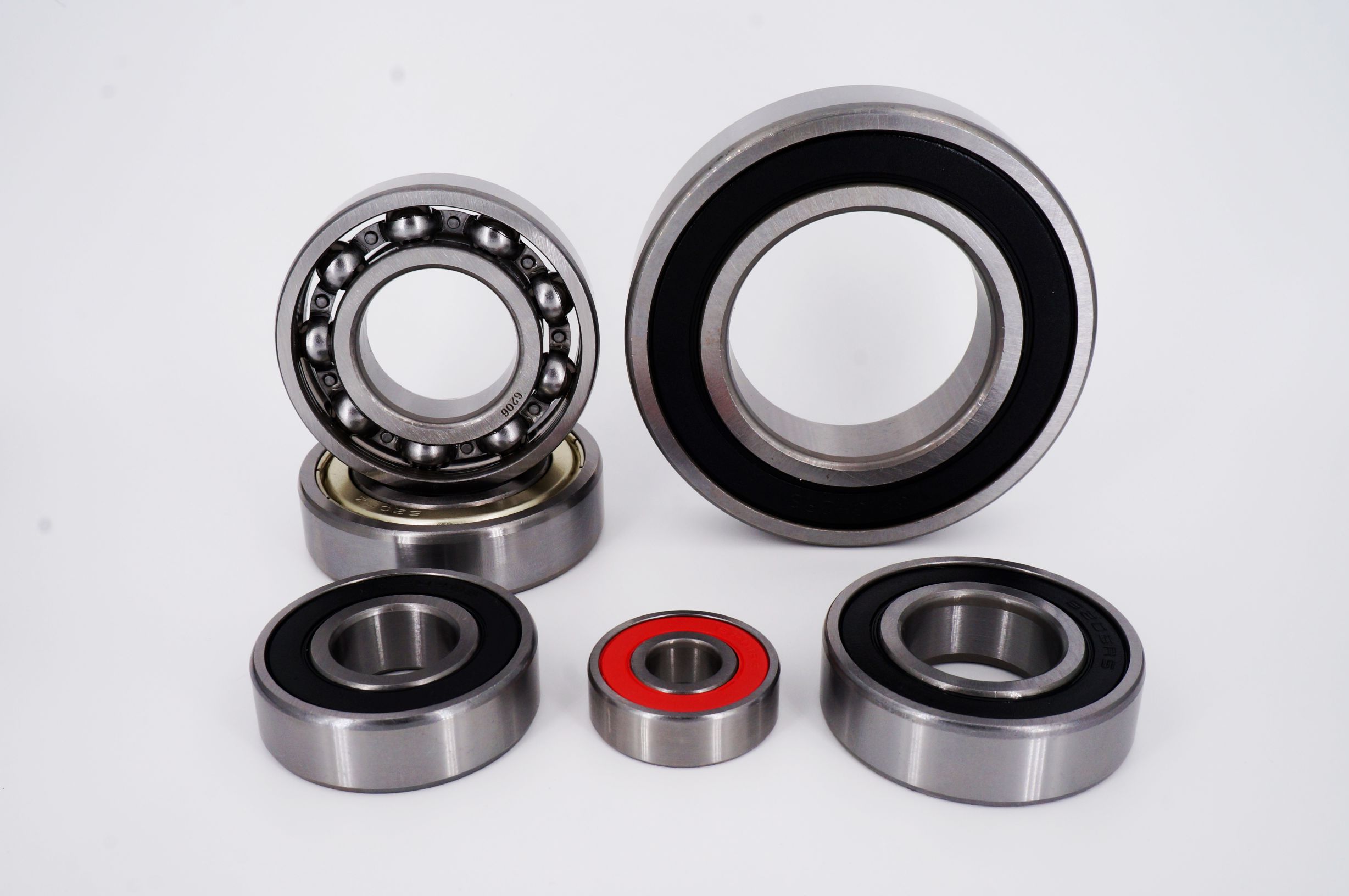
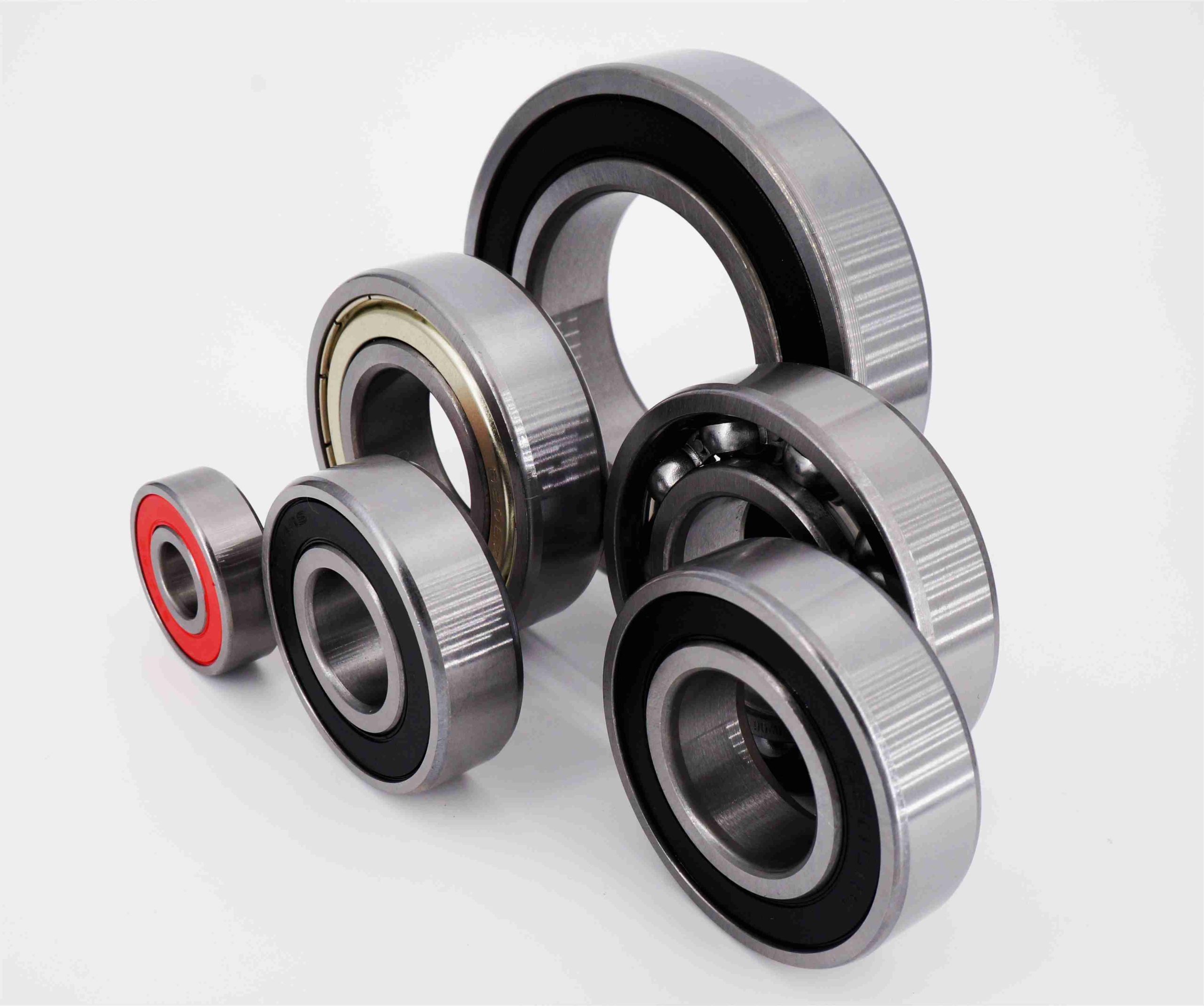
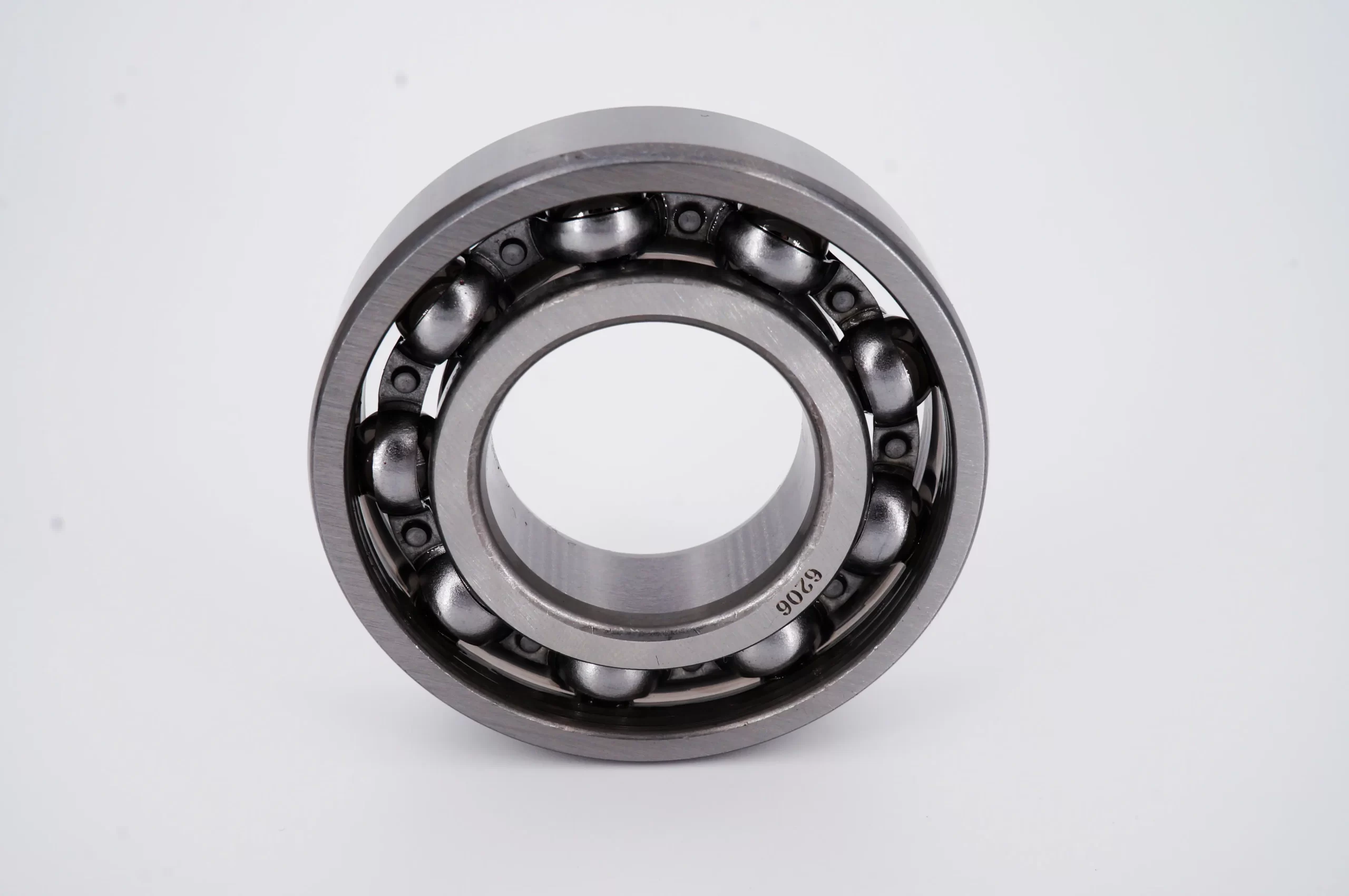
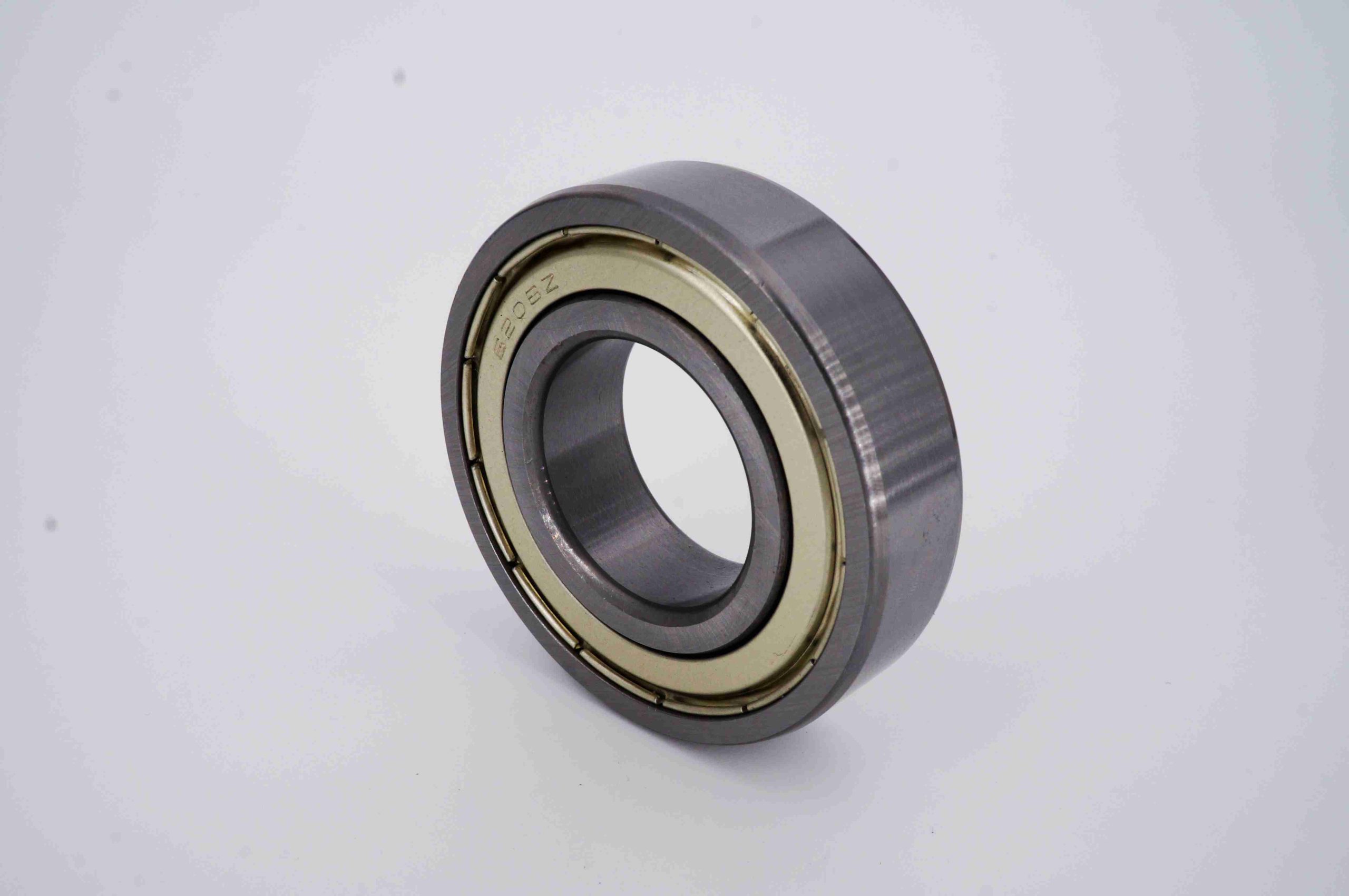
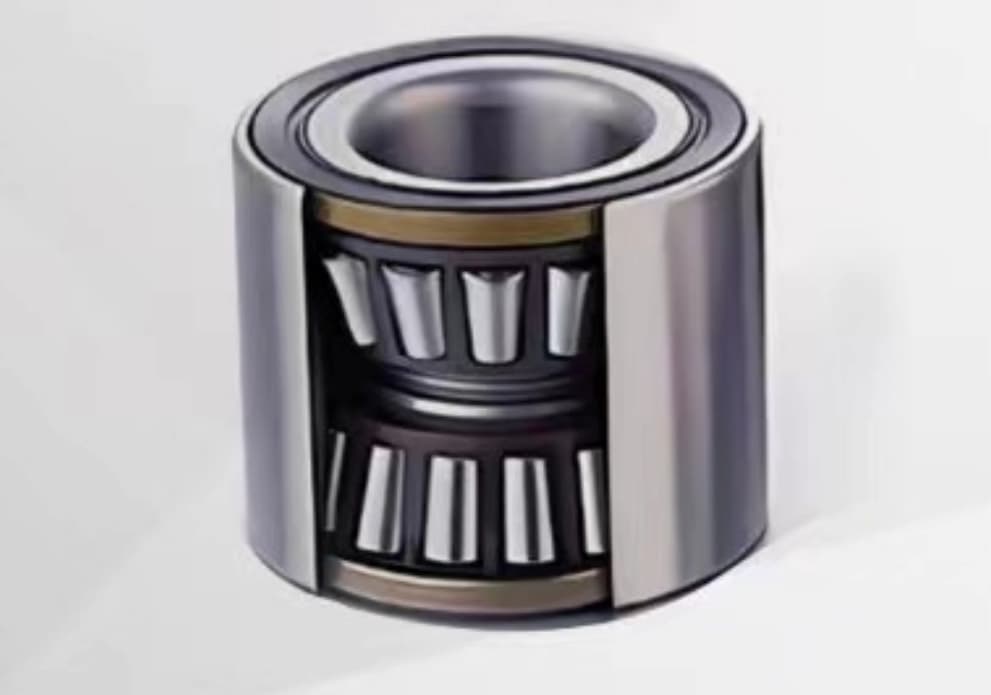
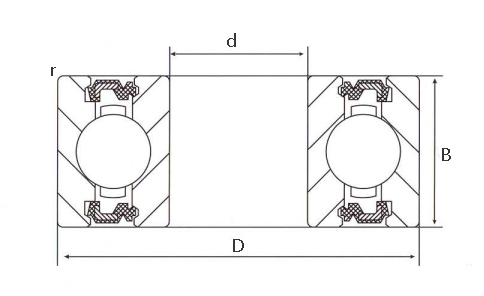
Deep groove ball bearing consists of the following key components:
- Inner Ring: This is the ring that fits onto the rotating shaft. It has a deep groove running along its outer surface to accommodate the balls.
- Outer Ring: This ring is stationary and fits into the bearing housing. Like the inner ring, it has a deep groove on its inner surface to house the balls.
- Balls: These are spherical rolling elements that fit between the inner and outer rings. The balls carry the load and allow the bearing to rotate smoothly.
- Retainer (or cage): This component separates the balls and evenly spaces them around the bearing. The retainer ensures that the balls are evenly distributed, reducing friction and wear.
- Seals or Shields (optional): Some deep groove ball bearings include seals or shields to protect the bearing from contaminants such as dust and moisture. Seals provide better protection but add some friction, while shields offer less protection but with lower friction.
The deep grooves in the inner and outer rings allow the balls to have greater contact with the raceways, enabling the bearing to handle higher loads and operate efficiently at high speeds.
Here are also some tips for Maintaining Deep Groove Ball Bearings below:
- Pravidelná kontrola:Periodically inspect the bearings for signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Check for unusual noise, vibration, or increased operating temperature, which can indicate issues.
- Proper Lubrication:Use the recommended type and amount of lubricant specified by the manufacturer. Re-lubricate the bearings at regular intervals to ensure smooth operation. Ensure the lubricant is clean and free of contaminants. For sealed bearings, ensure the seals are intact.
- Clean Environment:Keep the bearing and its surroundings clean to prevent contamination from dust, dirt, and moisture. Use proper sealing techniques to protect the bearing from external contaminants.
- Temperature Control:Monitor the operating temperature of the bearings. Excessive heat can reduce the bearing’s lifespan. Ensure proper ventilation and cooling in the bearing’s operating environment.
- Riadenie záťaže:Ensure the bearings are not subjected to excessive loads beyond their rated capacity. Avoid shock loads or sudden impacts that can damage the bearings. Distribute loads evenly to prevent localized stress on the bearing components.
- Alignment and Fit:Regularly check the alignment of the bearings to prevent misalignment, which can cause uneven wear. Ensure the bearing fits correctly within its housing and on the shaft.
- Handling and Storage:Handle bearings with care to avoid physical damage. Use clean gloves and avoid dropping or striking the bearings. Store bearings in a clean, dry environment to prevent corrosion and contamination.
- Replacement of Worn Bearings:Replace bearings that show signs of wear, damage, or reduced performance to prevent failure. Use the correct replacement bearings as specified by the manufacturer.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics:Utilize condition monitoring tools such as vibration analysis and temperature monitoring to detect early signs of bearing problems. Implement a preventive maintenance program to regularly check and maintain the bearings.
By following these maintenance tips, you can enhance the performance and extend the life of your deep groove ball bearings, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of your machinery.